Linearity
property
This property gives linear and
nonlinear circuit definition. The property can be applied in various circuit
elements. The homogeneity (scaling) property and the additive property are both
the combination of linearity property.The homogeneity property is that if the
input is multiplied by a constant k then the output is also multiplied by the
constant k. Input is called excitation and output is called response here. As
an example if we consider ohm’s law. Here the law relates the input i to the
output v.
Mathematically,
v= iR
If we multiply the input current i by a constant k then the output voltage
also increases correspondingly by the constant k. The equation stands,
kiR = kv
The additive property is that the
response to a sum of inputs is the sum of the responses to each input applied
separately.
Using voltage-current relationship of
a resistor if
v1 = i1R
and v2 = i2R
Applying (i1 + i2) gives
V = (i1 + i2) R = i1R+ i2R = v1 + v2
We can say that a resistor is a linear
element. Because the voltage-current relationship satisfies both the additive
and the homogeneity properties.
We can tell a circuit is linear if the
circuit both the additive and the homogeneous. A linear circuit always consists
of linear elements, linear independent and dependent sources.
What is
a linear circuit?

The linear circuit is excited by
another outer voltage source vs. Here the voltage source vs acts as input. The
circuit ends with a load resistance R. we can take the current I through R as
the output.
source transformation
Source transformation is simplifying a
circuit solution, especially with mixed sources, by transforming a voltage into
a current source, and vice-versa. Finding a solution to a circuit can be
difficult without using methods such as this to make the circuit appear
simpler. Source transformation is another tool
for simplifying circuits. Basic to these tools is the concept of equivalence.
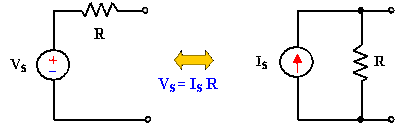
A
Source Transformation is the process of replacing a voltage source Vs in series
with a resistor R by a current source Is in parallel with a resistor R, or
vice-versa.
Source
transformation requires that,
Vs = IsR or Is = Vs/R
Source transformation also applies to
dependent sources, provided we carefully handle the dependent variable. As
shown in below, a dependent voltage source in series with a resistor can be
transformed to a dependent current source in parallel with the resistor or vice
versa.
OVERVIEW AND INSIGHTS
Linearity Property talks about the
voltage (v) and current (i), whereas voltage is directly proportional to the
current, that is, when the voltage is increasing the current also increasing and
vice-versa. I also learned that Source
Transformation is only applicable to simple circuits and not in a complicated
circuits.
Source Transformation can be applied
if and only if the voltage is in series with the resistor and/or the current is
in parallel with the resistor.
In Source Transformation you need to
check the polarity of the source, when the polarity of the voltage source has a
positive on top therefore the resulting current source is pointing upward and
vice-versa. Also when the voltage source is dependent therefore the resulting
current is also dependent, same calculations with independent sources.
Walang komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento